Melakarta ragams
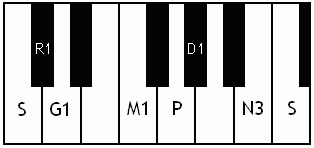
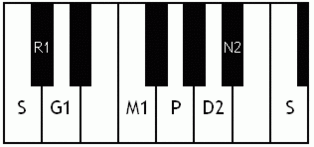
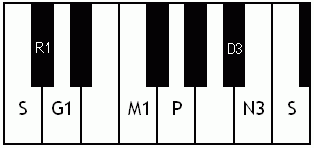
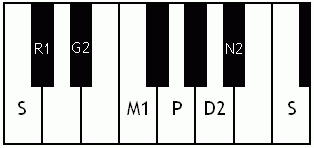
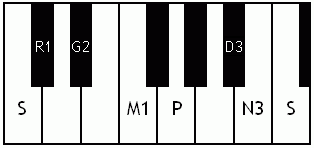
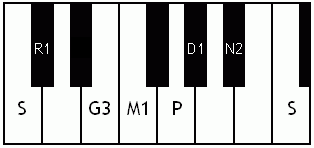
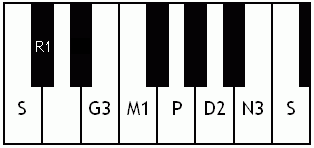
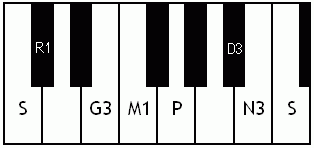
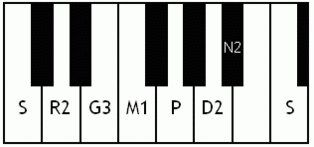
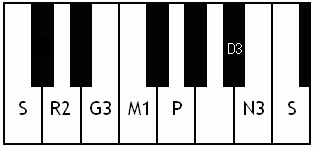
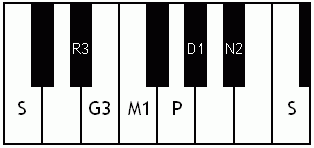
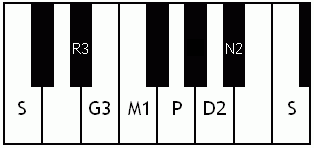
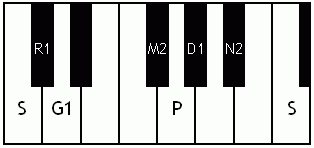
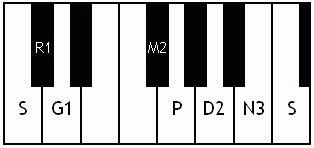
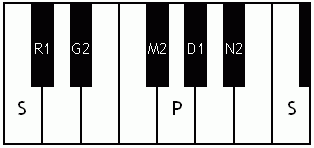
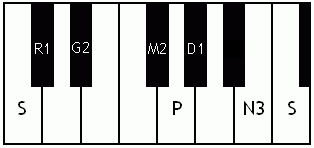
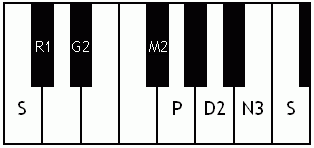
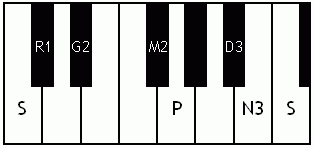
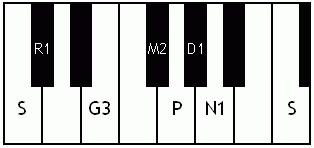
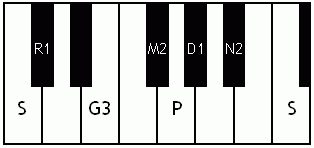
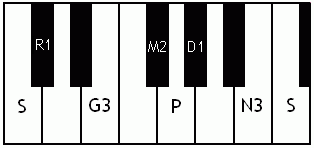
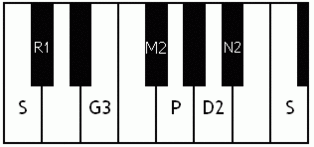
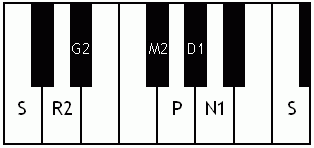
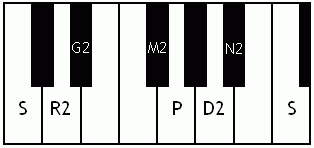
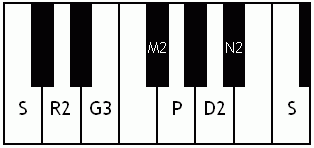
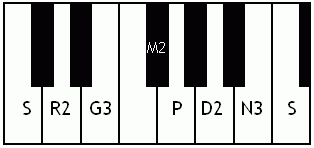
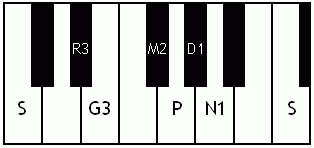
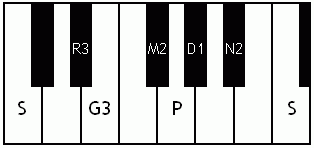
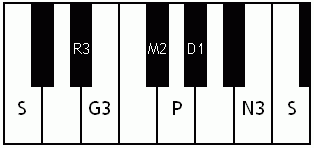
Notes of the Melakarta ragams in Carnatic music shown in a keyboard layout. In this image C is used as Shadjam for simplicity sake only. In Carnatic music any note can be the tonic note (sruti), which is taken as Shadjam note.

Each chakra (group) consists of 6 ragams. The Melakarta chart showing all the 72 Melakarta ragams and composite notes is shown to the right. The chart is a pictorial representation of the Katapayadi sankhya hashing scheme.
Note: Swaras in carnatic music are relative, while notes in western music are fixed. While for example Sa is depicted as C on the key board in the pictures below, it can start from any key..say a Cb or a C#..but the relative distance between the notes are maintained per the rules of that raga. You can hence find an equivalent western scale for all melakarta ragaas and many Janya raagas. However Janya raagas divert from the rules of western scales in one or more of the following ways
- 1. Aarohana and avarahona need not be the same
- 2. Aarohana and avarohana need not be linear ..i.e. you can have raagas like..Sa,Ga,Ri,Ga...for e.g.
Indu Chakra
[edit]-
English: Kanakangi the first Melakarta
-
English: Ratnangi the 2nd Melakarta
-
English: Ganamoorti the 3rd Melakarta
-
English: Vanaspati the 4th Melakarta
-
English: Manavati the 5th Melakarta
-
English: Tanaroopi the 6th Melakarta
Netra Chakra
[edit]-
English: Senavati the 7th Melakarta
-
English: Hanumatodi the 8th Melakarta, popularly known as Todi
-
English: Dhenuka the 9th Melakarta
-
English: Natakapriya the 10th Melakarta
-
English: Kokilapriya the 11th Melakarta
-
English: Roopavati the 12th Melakarta
Agni Chakra
[edit]-
English: Gayakapriya the 13th Melakarta
-
English: Vakulabharanam the 14th Melakarta
-
English: Mayamalavagowla the 15th Melakarta
-
English: Chakravakam the 16th Melakarta
-
English: Sooryakantam the 17th Melakarta
-
English: Hatakambari the 18th Melakarta
Veda Chakra
[edit]-
English: Jhankaradhwani the 19th Melakarta
-
English: Natabhairavi the 20th Melakarta
-
English: Keeravani the 21st Melakarta
-
English: Kharaharapriya the 22nd Melakarta
-
English: Gourimanohari the 23rd Melakarta
-
English: Varunapriya the 24th Melakarta
Bana Chakra
[edit]-
English: Mararanjani the 25th Melakarta
-
English: Charukesi the 26th Melakarta
-
English: Sarasangi the 27th Melakarta
-
English: Harikambhoji the 28th Melakarta
-
English: Shankarabharanam the 29th Melakarta
-
English: Naganandini the 30th Melakarta
Ritu Chakra
[edit]-
English: Yagapriya the 31st Melakarta
-
English: Ragavardini the 32nd Melakarta
-
English: Gangeyabhooshani the 33rd Melakarta
-
English: Vagadheeshwari the 34th Melakarta
-
English: Shoolini the 35th Melakarta
-
English: Chalanata the 36th Melakarta
Rishi Chakra
[edit]-
English: Salagam the 37th Melakarta
-
English: Jalarnavam the 38th Melakarta
-
English: Jhalavarali the 39th Melakarta
-
English: Navaneetam the 40th Melakarta
-
English: Pavani the 41st Melakarta
-
English: Raghupriya the 42nd Melakarta
Vasu Chakra
[edit]-
English: Gavambhodi the 43rd Melakarta
-
English: Bhavapriya the 44th Melakarta
-
English: Shubhapantuvarali the 45th Melakarta
-
English: Shadvidamargini the 46th Melakarta
-
English: Suvarnangi the 47th Melakarta
-
English: Divyamani the 48th Melakarta
Brahma Chakra
[edit]-
English: Dhavalambari the 49th Melakarta
-
English: Namanarayani the 50th Melakarta
-
English: Kamavardini the 51st Melakarta
-
English: Ramapriya the 52nd Melakarta
-
English: Gamanashrama the 53rd Melakarta
-
English: Vishwambari the 54th Melakarta
Disi Chakra
[edit]-
English: Shamalangi the 55th Melakarta
-
English: Shanmukhapriya the 56th Melakarta
-
English: Simhendramadhyamam the 57th Melakarta
-
English: Hemavati the 58th Melakarta
-
English: Dharmavati the 59th Melakarta
-
English: Neetimati the 60th Melakarta
Rudra Chakra
[edit]-
English: Kantamani the 61st Melakarta
-
English: Rishabhapriya the 62nd Melakarta
-
English: Latangi the 63rd Melakarta
-
English: Vachaspati the 64th Melakarta
-
English: Mechakalyani the 65th Melakarta
-
English: Chitrambari the 66th Melakarta
Aditya Chakra
[edit]-
English: Sucharitra the 67th Melakarta
-
English: Jyotiswaroopini the 68th Melakarta
-
English: Dhatuvardani the 69th Melakarta
-
English: Nasikabhooshani the 70th Melakarta
-
English: Kosalam the 71st Melakarta
-
English: Rasikapriya the 72nd Melakarta