Jewish history
Appearance
English: Jewish history
The main category is: Category:Jewish history

Origins
[edit]-
Abraham Journeying into the Land of Canaan
-
Moses on the Knesset Menorah
-
Mountains in Sinai, traditional region for the Israelite theophany
-
Egyptian image of ibrw "mounted bowmen" at the Battle of Kadesh 1274 BCE, one suggested origin for Hebrew
-
Merneptah Stele, 1213-1203 BCE, first recorded extra-Biblical mention of Israel
-
12 Tribes of Israel according to the Book of Joshua
-
Rock hewn altar near Shiloh, early site of the Tabernacle in Israel
-
Ruth on the Knesset Menorah, convert from Moab, traditional anscestor of David
First Commonwealth
[edit]-
Walls of the Jebusite city of Jerusalem prior to David's conquest in 1000 BCE
-
Solomon's temple in Jerusalem
-
10th century BCE inscription showing the conquest of Judah (Yuteh Malek) by Shoshenq I
-
Divided Kingdoms of Israel and Judah in their region, 9th century BCE
-
Mesha Stele from Moab c.840 BCE, extensive description of Kingdom of Israel
-
King Jehu of Israel giving tribute to King Shalmaneser III of Assyria, on the Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser c.827 BCE
-
Biblical genealogy of kings of Israel and Judah described in 1 and 2 Kings
-
Reconstructed Israelite house, 10th–7th centuries BCE
-
Isaiah on the Knesset Menorah
-
King Hezekiah's tunnel in Jerusalem, 8th-7th centuries BCE
-
Judean captives led to slavery by the Assyrians after the siege of Lachish in 701 BCE
-
Tetragrammaton name of God in Paleo-Hebrew from Tel Lachish
-
Ten Lost Tribes of northern kingdom deportated to Assyria, 734-715 BCE
Babylonian and Persian exile
[edit]-
Jeremiah on the Knesset Menorah, who predicted the destruction of Jerusalem
-
Kingdom of Judah exiled to Babylon and destruction of Solomon's temple in 587 BCE
-
City of Babylon during the time of the Nebuchadnezzar II, 600 BCE
-
At the Rivers of Babylon (Psalm 137)
-
Ezekiel's vision in exile of the restored bones of Israel
-
Persian Empire, who conquered Babylon, around the time of Darius and Xerxes
-
Hand-written scroll of the Book of Esther, set in Persian Empire
Early Second Commonwealth
[edit]-
Ezra on the Knesset Menorah
-
Nehemia on the Knesset Menorah
-
Yehud coins from the Persian Empire province of Judah
-
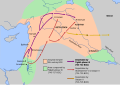
Alexander the Great's empire and his route 334-323 BCE
-
Hellenistic enforcement of Seleucid Greek king Antiochus IV Epiphanes with Apollo
-
Tombs of the Maccabees national revolt against Seleucid Hellenism 167–160 BCE
-
Hasmonian dynasty rulers from the Maccabees until the time of Herod
-
Coin of Alexander Jannaeus 103-76 BCE, whose opposition to the Pharisees formented the Judean Civil War
Roman Empire
[edit]-
Early Rabbinic sage Hillel on the Knesset Menorah
-
One of the Dead Sea Scrolls, discovered between 1946 and 1956
-
Model of Herod's rebuilt Jerusalem temple
-
Philo of Alexandria c.20 BCE–50 CE, Hellenistic Jewish philosopher and influence on Christianity
-
Helena of Adiabene sarcophagus, 1st century queen of Adiabene and convert to Judaism, Jerusalem
-
Roman sack of Jerusalem in 70 CE depicted on the Arch of Titus
-
Translation of 1st century Jewish historian Josephus
-
Johanan ben Zakai, c.30-90 CE, re-established the Rabbinic Sanhedrin in Yavne after Jerusalem's destruction
-
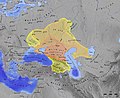
The Roman Empire at its greatest extent in 117 CE
-
Tunnels from the Bar Kokhba revolt of 132–136 CE
-
Haninah ben Teradion, 2nd century sage martyred by the Romans
-
Coin of Hadrian 136 CE, changing Jerusalem into pagan city Aelia Capitolina banned to Jews
-
Map of 1st-2nd century CE synagogues in the Mediterranean world
-
Roman Jewish fresco from Dura Europos synagogue, Syria, 244 CE. Destroyed by Sassanids 256 CE
Late Antiquity and Early Middle Ages
[edit]-
Babylonian Talmud on the Knesset Menorah
-
Aggadah Rabbinic Midrash on the Knesset Menorah
-
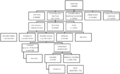
Schematic map of the Oral Torah development from the Pharisees to Halakha
-
Exhibit showing Talmudic sage and Exilarch political leader in Babylonia, Rav Huna
-
An emissary from the land of Israel is a Sabbath guest in Nehardea, Babylonia
-
Byzantine era mosaic from synagogue near Sea of Galilee, 5th-6th century
-
6th century underground mikvah Jewish ritual bath in Syracuse, Italy
-
Mohammed defeating the Banu Nadir Jewish tribe at Medina, 14th century art
-
Khazar Khaganate, 650–850. From the 8th century, the Khazar royalty and parts of the aristocracy converted to Judaism
-
8th-9th century Hebrew Selihah prayer, discovered in 1908 in the Dunhuang Caves of Gansu Province, China
High and Late Middle Ages
[edit]-
Rashi house in Worms, Germany
-
Golden Age of Spanish Jewry: codifier and philosopher Maimonides, and Jewish poets
-
Babylonian Talmud manuscript with commentaries from France, 1342
-
1348 Barcelona manuscript of Maimonides' philosophical Guide for the Perplexed
-
Statues of "Church" victorious and "Synagogue" defeated from Strasbourg Cathedral 12-13th centuries
-
Woodcut of disputation between Christian and Jewish scholars, which were often forced on Medieval Jews
-
Expulsions of Jews in Europe from 1100 to 1600
-
Medieval Passover Haggadah found in the Cairo Genizah
-
Sarajevo Haggadah manuscript from 14th century Spain
-
Amulet text from 15th century Jewish magic work
Early modern era
[edit]-
The Venice Ghetto, instituted 1516, gave its name to other Jewish restricted quarters in Europe
-
Title page of first edition of the kabbalistic Zohar, printed Mantua Italy 1558
-
Synagogue in Safed, Galilee, 16th century centre of Jewish religious renaissance
-
Baruch Spinoza, 1632–1677, Dutch philosopher and secular Jewish forerunner
-
Hope for the Messiah on the Knesset Menorah
-
The mystical heresy of Sabbatai Zevi, Messianic claimant of 1665-1666, broke Jewish unity
-
Portuguese Synagogue in Amsterdam, built 1675
-
Council of the Four Lands, gave Poland Rabbinic autonomy
-
Synagogue of the Baal Shem Tov, 1700s founder of Hasidic movement mystical revival in Ukraine
-
Moses Mendelssohn, founder of Haskalah Jewish modernism, with German playwrite Lessing
-
Vilna Gaon, figurehead of Lithuanian-Yeshiva Talmudic movement
-
Illuminated Ketubah marriage contract from Yemen, 1795
19th century
[edit]-
1806 French print of Napoleon emancipating the Jews
-
Crimean Karaites, followers of non-Rabbinic Judaism originating 8th century CE, shown in 1837
-
The Hamburg Temple, first reform synagogue in Germany, location 1818–1844
-
Leopold Zunz, 1794–1886, founder of Wissenschaft des Judentums 19th century historical-critical investigation of Judaism
-
Samson Raphael Hirsch, 1808–1888, founder of Neo-Orthodox Judaism and leader of German Orthodox secessionist communities
20th century
[edit]-
Theodor Herzl, Zionist founder, in 1901
-
Belarus stamp with shtetl painting of Marc Chagall, 1887–1985
-
Eliezer Ben-Yehuda, reviver of the Hebrew language, in Jerusalem 1912
-
Simon Dubnow, 1860–1941, Jewish historian and activist, founder of the Yiddish culture East-European Jewish folkists party
-
Sigmund Freud's psychoanalytical circle, 1922, reflecting assimilated Jewish culture of Vienna
-
Israeli currency portrait of Ze'ev Jabotinsky, 1880–1940, founder of Israel's right-wing secular politics
-
Martin Buber, philosopher and cultural Zionist, teaching at the Hebrew University Jerusalem
-
Religious anti-Zionist and pro-Zionist Rabbis Sonnenfeld, and Kook, the first chief Rabbi of Palestine and founder of Religious Zionism, early 1930s
-
Menorah in Birobidzhan, Jewish Autonomous Oblast in Russian Far East, established by Stalin 1934
-
WW2 propaganda
-
Warsaw Ghetto uprising in April 1943
-
Yemenite immigrants celebrating Passover, Tel Aviv 1946
-
Exodus ship carrying Jewish emigrants to Palestine in 1947
-
Israeli tanks crossing the Suez Canal in the 1973 Yom Kippur War
-
Israeli - Palestinian Oslo Accords in 1993
-
Diaspora Museum Tel Aviv. Exhibit "One culture: Many facets. The growth of pluralism in modern Jewish spiritual life"