File:01 Die grasende Ziege-3.svg

Original file (SVG file, nominally 908 × 650 pixels, file size: 98 KB)
Captions
Captions
Contents
Summary[edit]
| Description01 Die grasende Ziege-3.svg |
Deutsch: Die grasende Ziege (Das Ziegenproblem)
English: The grazing goat (The goat problem) |
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | Petrus3743 |
| SVG development InfoField |
Siehe auch[edit]
Konstruktion[edit]

 ist quasi der Pfosten an dem die Ziege mit einem Seil der Länge
ist quasi der Pfosten an dem die Ziege mit einem Seil der Länge  angebunden ist.
angebunden ist.- Einheitskreis (grün) um
mit Radius
.
- Gerade durch
und
ergibt Schnittpunkt
.
- Gerade senkrecht zu
durch
ergibt Schnittpunkte
und
.
- Strecken
.
- Strecken
, Kreis um
durch
ergibt Schnittpunkt
und Kreis um
durch
ergibt Schnittpunkt
.
- Bestimmen der Funktionspunkte:
- Es beginnt mit Punkt
, dessen Abstand zu Punkt
ist gleich der Strecke
. In der Darstellung beschrieben als
. Auf diese Art und Weise werden auch die weiteren Funktionspunkte von
als
bis
als
(Reihenfolge siehe Kurzbeschreibung in der Darstellung) festgelegt.
- Es beginnt mit Punkt
- Einzeichnen der Kreissekanten:
- Es beginnt mit der Sekante ab
durch
bis sie die äußere Kreislinie in
schneidet. Die nächste Sekante läuft ab dem zuletzt erhaltenen Schnittpunkt
durch
bis sie ebenfalls die äußere Kreislinie in
schneidet. Auf diese Art und Weise werden auch die Punkte von
bis
(Reihenfolge ist anhand des Verlaufs der Sekanten zu entnehmen) bestimmt.
- Es beginnt mit der Sekante ab
- Letzte Sekante von
durch
schneidet die äußere Kreislinie in
.
- Der abschließende Kreisbogen um
mit Radius
schneidet den Einheitskreis (grün) in
und
. Somit ist die kreisförmige Wiesenfläche nahezu halbiert.

The goat problem, construction as an animation
Ergebnis[edit]
- Der in GeoGebra konstruierter Radius
(Anzeige max. 15 Nachkommastellen).
- Die Berechnung ergibt
(Folge A133731 in OEIS).
- Der absolute Fehler des konstruierten Radius
ist in GeoGebra aufgrund der Anzeigebegrenzung nicht verifizierbar.
Beispiel um den Fehler zu verdeutlichen[edit]
Bei einem Umkreisradius r = 1 Mrd. km (das Licht bräuchte für diese Strecke ca. 55 min), wäre der absolute Fehler des konstruierten Radius 
See also[edit]
Construction[edit]

 is like the vertical member to which the goat is tied with a rope of length
is like the vertical member to which the goat is tied with a rope of length  .
.- Unit circle (green) around
with radius
.
- Straight line through
and
yields intersection
.
- Straight line perpendicular to
through
yields intersections
and
.
- Line segments
.
- Line segments
, circle around
through
yields intersection
and circle around
through
gives intersection
.
- Determining the function points:
- It starts with point
, whose distance to point
is equal to the segment
. Described in the representation as
. In this way, the other function points from
as
to
as
(sequence see short description in the representation).
- It starts with point
- Drawing in the circle secant:
- It starts with the secant from
through
until it intersects the outer circle at
. The next secant runs from the last received intersection
through
until it also intersects the outer circle line in
. In this way, the points from
to
(order can be seen from the progression of the secants) are determined.
- It starts with the secant from
- Last Secant of
through
intersects the outer circle in
.
- The final arc around
with radius
intersects the unit circle (green) in
and
. Thus, the circular meadow area is almost halved.
Result[edit]
- The radius constructed in GeoGebra
(display max. 15 decimal places).
- The calculation results in
(sequence A133731 in OEIS).
- The absolute error of the constructed radius
is not verifiable in GeoGebra due to the display limitation.
Example to clarify the error[edit]
With a radius of r = 1 billion km (the light would need about 55 min for this distance), the absolute error of the constructed radius 
Licensing[edit]
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 17:52, 5 April 2022 |  | 908 × 650 (98 KB) | Petrus3743 (talk | contribs) | Strecke AF ergänzt |
| 14:05, 5 April 2022 | 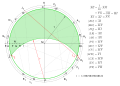 | 910 × 650 (96 KB) | Petrus3743 (talk | contribs) | Uploaded own work with UploadWizard |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
The following 2 pages use this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| Width | 908.107 |
|---|---|
| Height | 650.414 |